Laboratory Fume Hood Functional Guide

In the chemical laboratory, various harmful odorous gases, odors, moisture and corrosive substances will be generated during the experimental operation. In order to protect the safety of users and prevent the pollutants in the experiment from spreading to the laboratory, it should be used fume hood near the pollution source. Fume Hood is used to protect lab environment and operator during general chemical applications. It actively protects operator from inhaling toxic vapors and dramatically reduces the risk of fire and explosion. By installing proper filter, it can also protect environment.
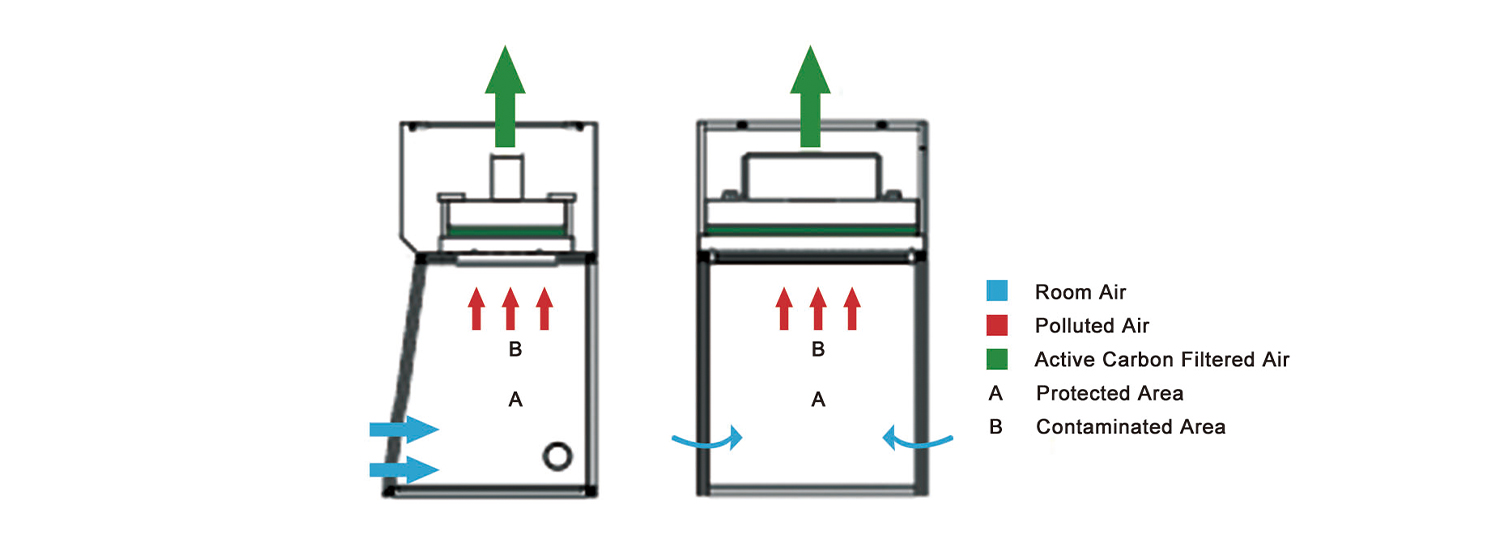
The biggest purpose of using a fume hood is to discharge the harmful gases generated in the experiment and protect the health of the experimenters, that is to say, there must be a high degree of safety and superior operability during the experiment, which requires the fume hood to have the following functions:
(1) Release function: The fume hood should be equipped to dilute the harmful gas generated inside the hood by absorbing the gas outside the hood and then discharge it to the outside.
(2) Non-reverse flow function: The fume hood shall have a function so that the airflow produced by the exhaust fan does not reverse the flow of harmful gases from the inside of the fume hood into the room.
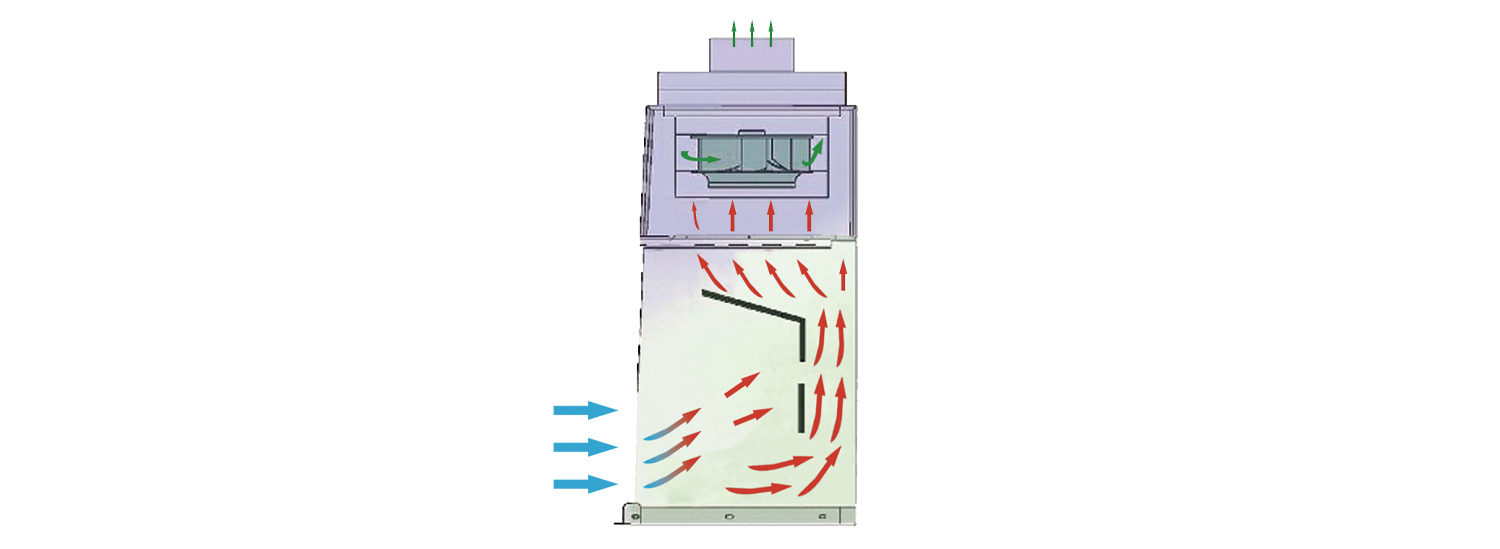
(3) Isolation function: In front of the fume hood, a non-slip glass window should be used to separate the inside and outside of it.

(4) Supplementary function: The fume hood shall have a passage or alternative device means to draw in air from the outside when the harmful gas is discharged.
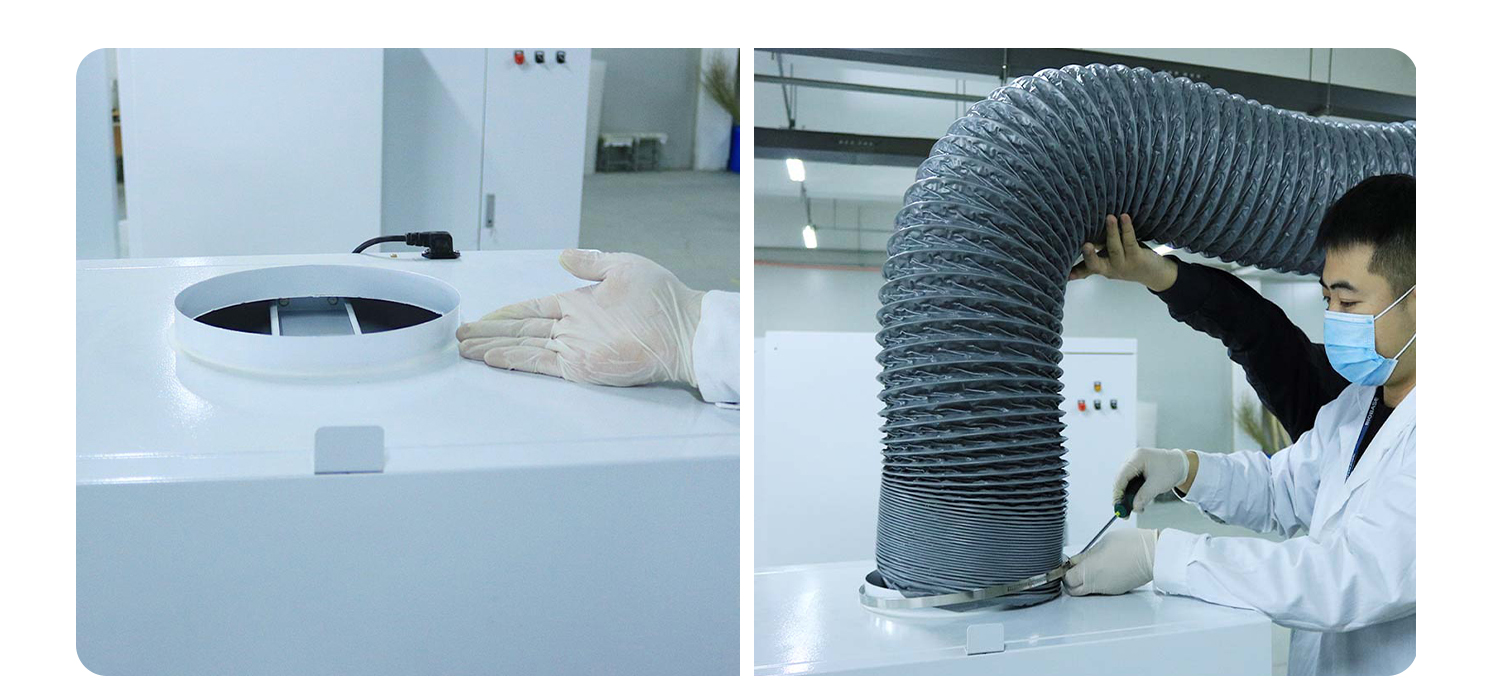

(5) Controlling wind speed function: In order to prevent harmful gases from escaping, the fume hood needs to have a certain intake speed. The factor that determines the intake speed of the air inlet is the relationship between the heat generated by the experimental content and the number of air changes, which is mainly determined by the experimental content and the nature of the harmful substances. It is generally stipulated that the intake speed of non-toxic pollutants is 0.25-0.38m/s, toxic or dangerous harmful substances are 0.4-0.5 m/s, highly toxic or a small amount of radioactivity is 0.5-0.6m/s, and gaseous substances are 0.5m/s, and the granular material is 1m/s. In order to ensure such a wind speed, the exhaust fan should have the necessary static pressure, that is, the frictional resistance of the air when it passes through the ventilation duct.

(6) Heat resistance and acid and alkali corrosion resistance function: Some of the fume hoods need to be installed with electric furnaces, and some experiments produce a large amount of toxic and harmful gases such as acid and alkali, which are extremely corrosive. Therefore, the countertop, lining plate, side plate and the selected water nozzle and gas nozzle of the fume hood should have anti-corrosion function. In the semiconductor industry or in corrosive experiments where strong acids such as sulfuric acid, nitric acid, and hydrofluoric acid are used, it is also required that the overall material of the fume hood must be resistant to acid and alkali, and be made of stainless steel or PVC.
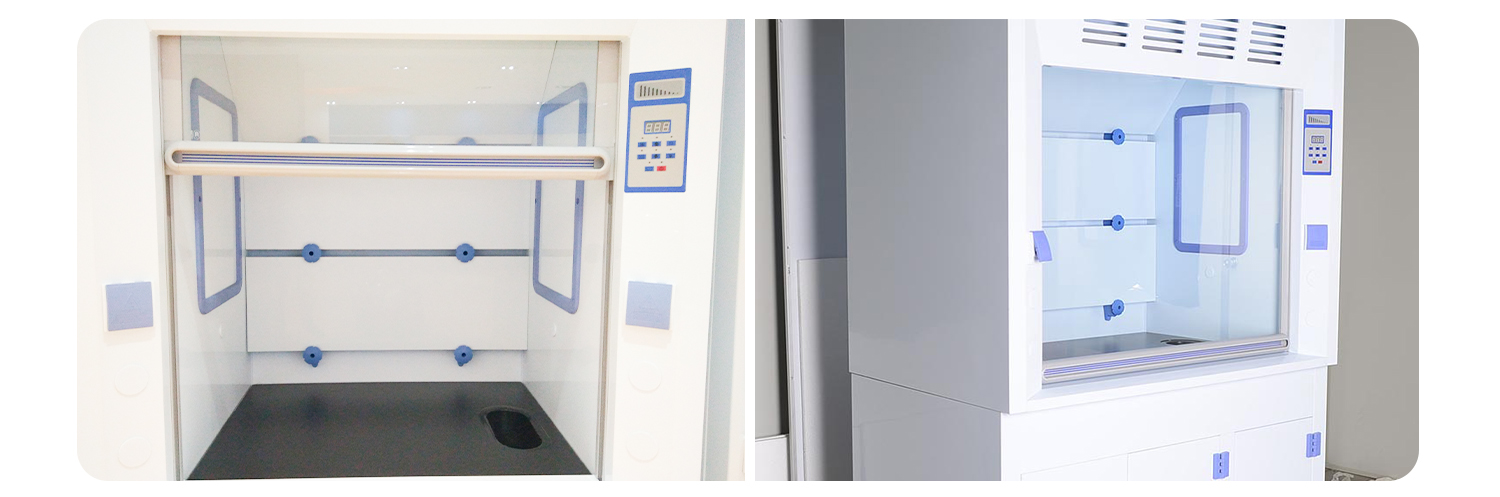

Safety is the primary consideration of fume hoods, and it is with the above functions that fume hoods are of great value in laboratory configurations.
